
hand anatomy featured Brace Access
These nerves merge to form a network called the brachial plexus before continuing into the arm. Five major nerves extend from the brachial plexus into the arm: the axillary, musculocutaneous, median, radial, and ulnar nerves. Each of these nerves carries information in the form of nerve impulses to and from a particular region of the arm and hand.
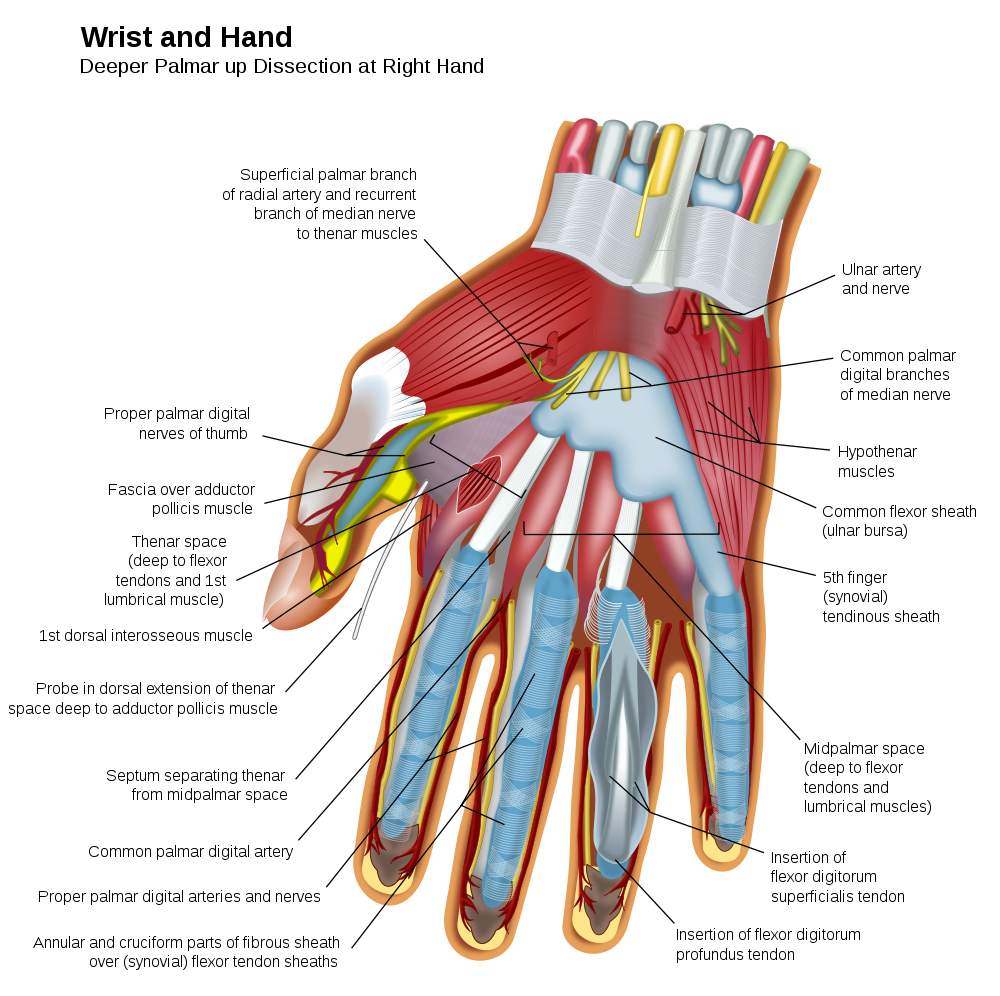
BY 411 Advanced Human Anatomy Blog February 2011
Based on the above, a simple way of sketching the hand is to start with the basic form of the palm, a flat shape (very much like a steak, but roundish, squarish, or trapezoidal) with rounded angles, then attach the fingers : If you have a hard time drawing fingers, it's very helpful to think of them, and draw them, as stacks of three cylinders.

Detailed Hand Reflexology Map
Anatomy Where are the hand and wrist located? Your wrist is the joint at the end of your forearm. It's the hinge between your arm and hand that lets you reposition your hand. Your hand begins where your wrist ends. It includes your palm, fingers and thumb. Advertisement How are the hand and wrist structured?

Understanding the Anatomy of the Hand Health Life Media
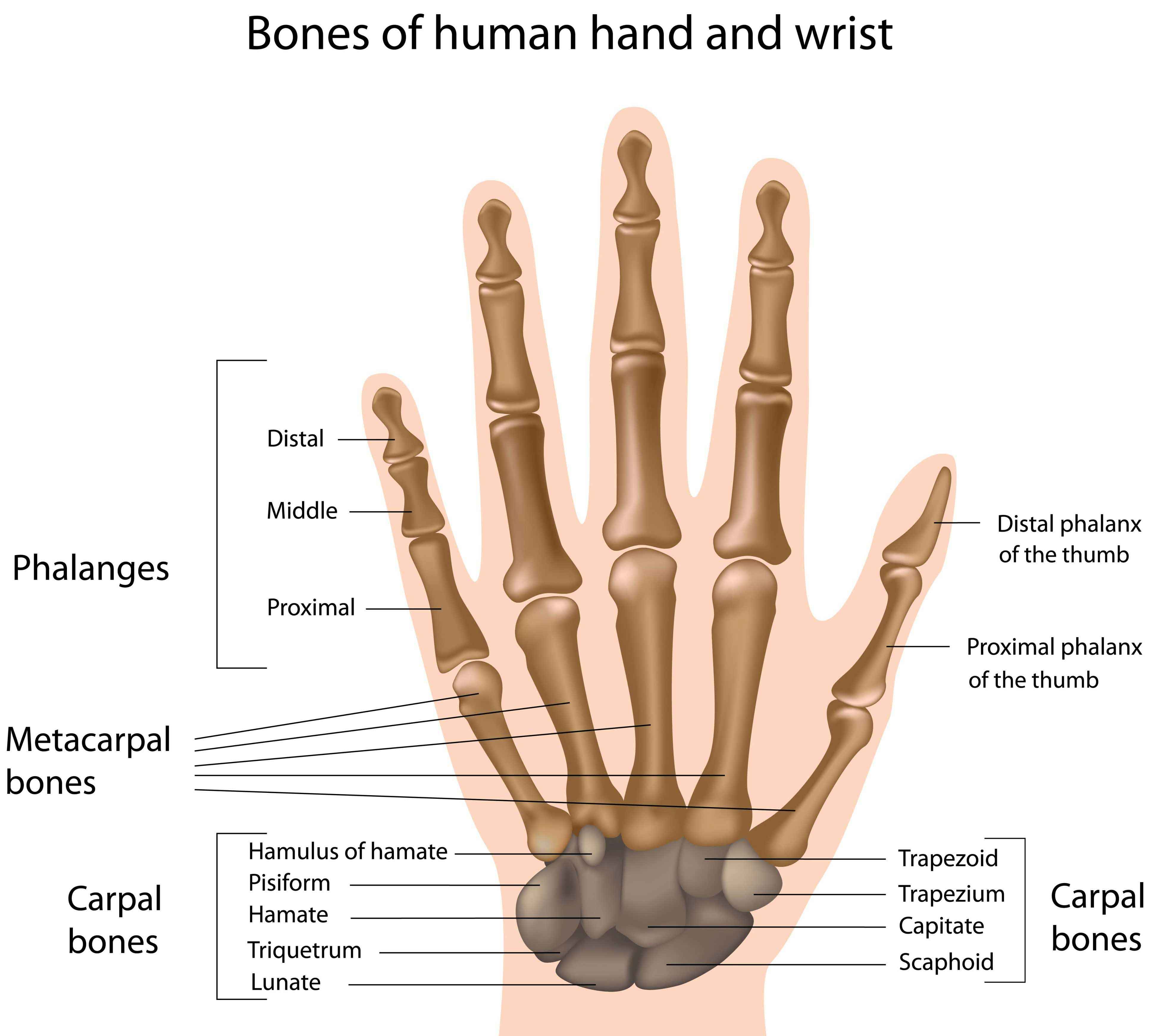
Phalanges of hand (Phalanges manus) The phalanges of the hand are the group of small bones that comprise the bony core of the digits (fingers) of the hand.Even though the phalanges are small in size, they are classified as long bones because of their structural characteristics; each phalanx consists of a shaft, distal head and a proximal base.. There are fourteen phalanges in each hand; each.
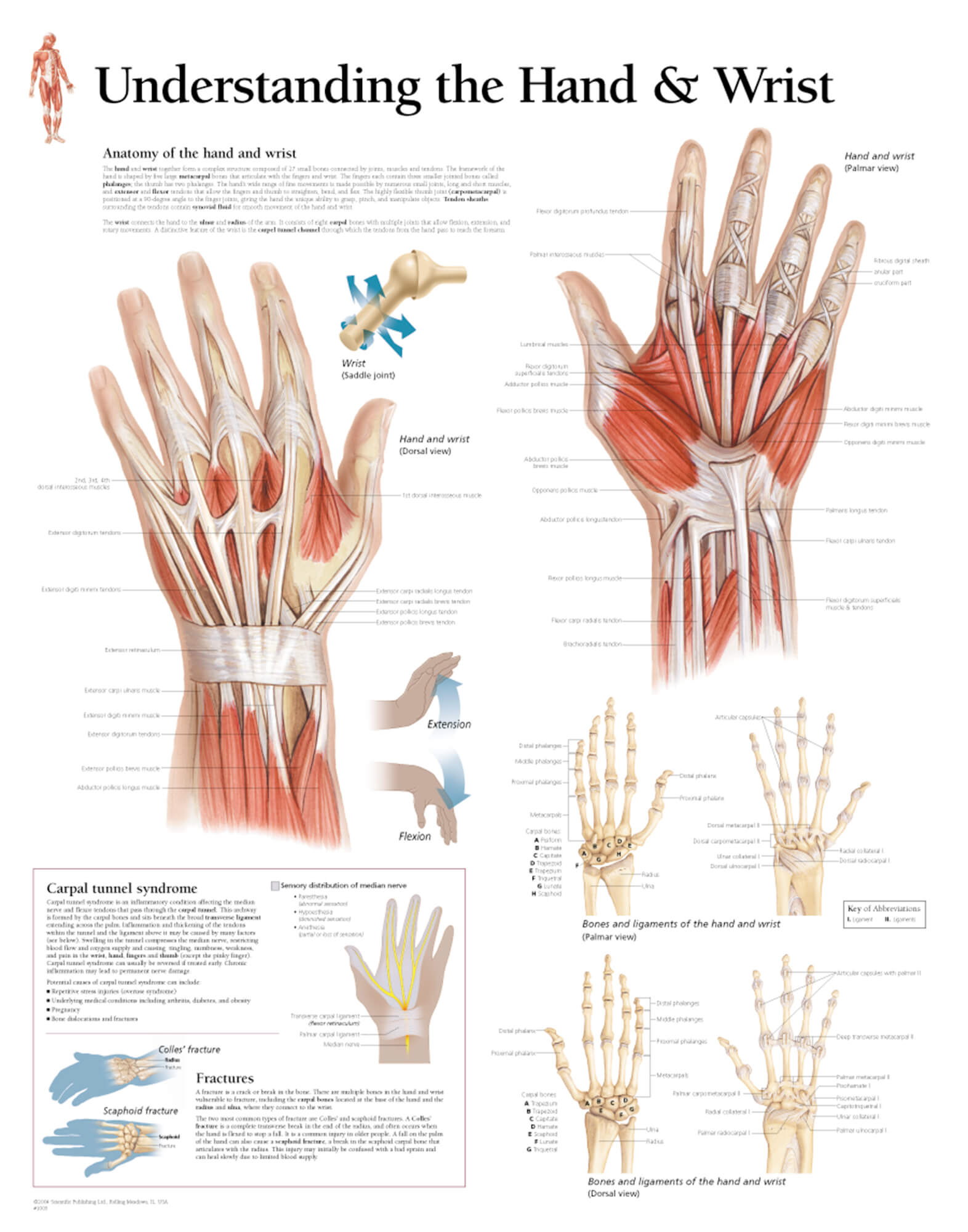
Understanding the Hand & Wrist Scientific Publishing
Hand anatomy Author: Adrian Rad BSc (Hons) • Reviewer: Nicola McLaren MSc Last reviewed: November 13, 2023 Reading time: 14 minutes Recommended video: Bones of the wrist and hand [23:54] Overview of the bones of the hand and wrist. Hand (dorsal view)
Diagram showing human hands 444634 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate strength forms the basis for normal hand function. The hand also must be coordinated to perform fine motor tasks with precision.

Human body Human bones, Hand anatomy, Human skeleton parts
Last Updated On June 29, 2021 by Dr. Andrew Chung The wrist links the hand to the forearm. The wrist is a complex system of many small bones (known as the carpal bones) and ligaments. The carpal bones are arranged in 2 interrelated rows. One row connects with the ends of the bones in the forearm—the radius and ulna.
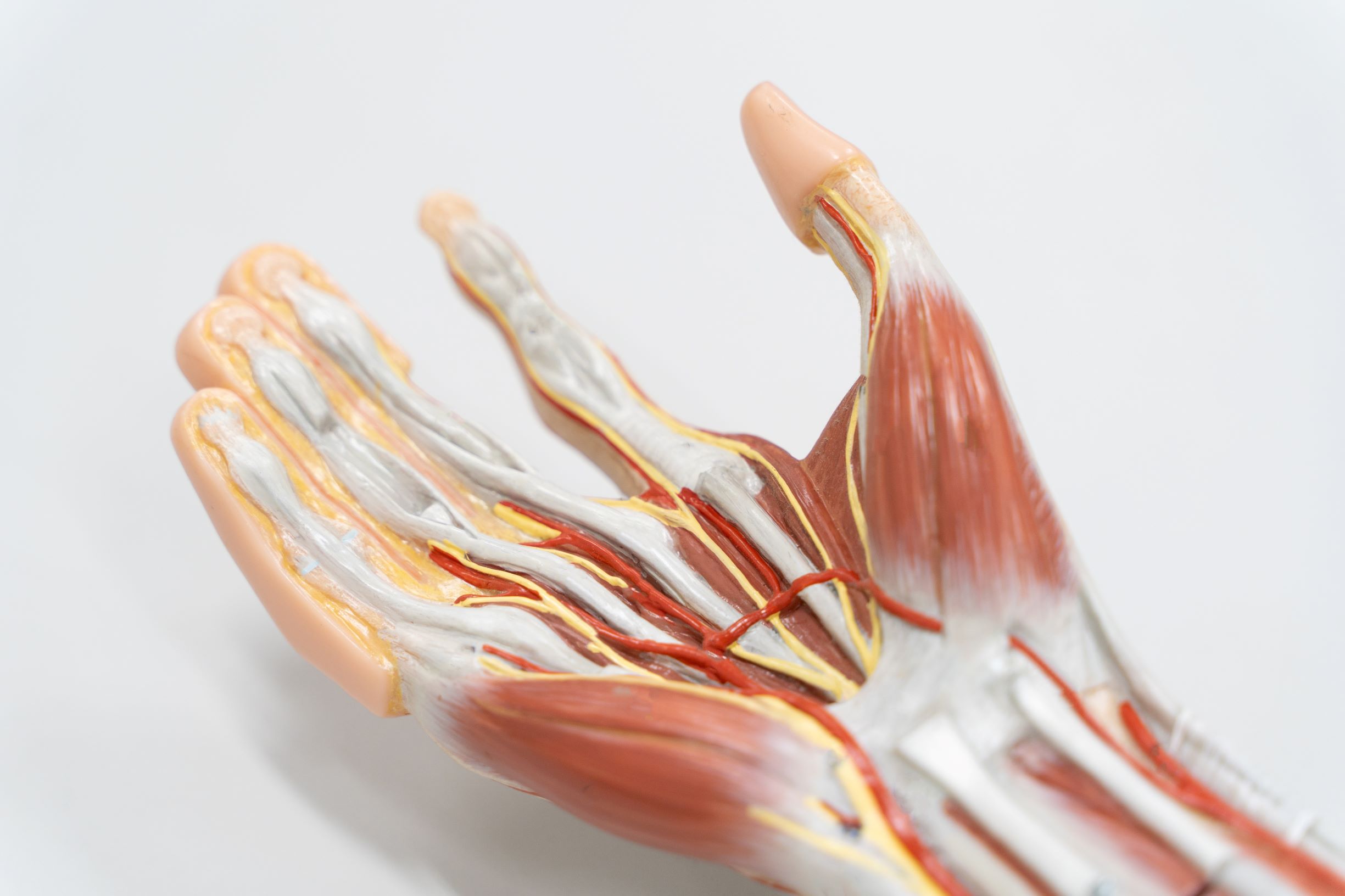
How Many Muscles are in the Hand? Arora Hand Surgery
Palm. The palm comprises the underside of the human hand. Also known as the broad palm or metacarpus, it consists of the area between the five phalanges (finger bones) and the carpus (wrist joint.
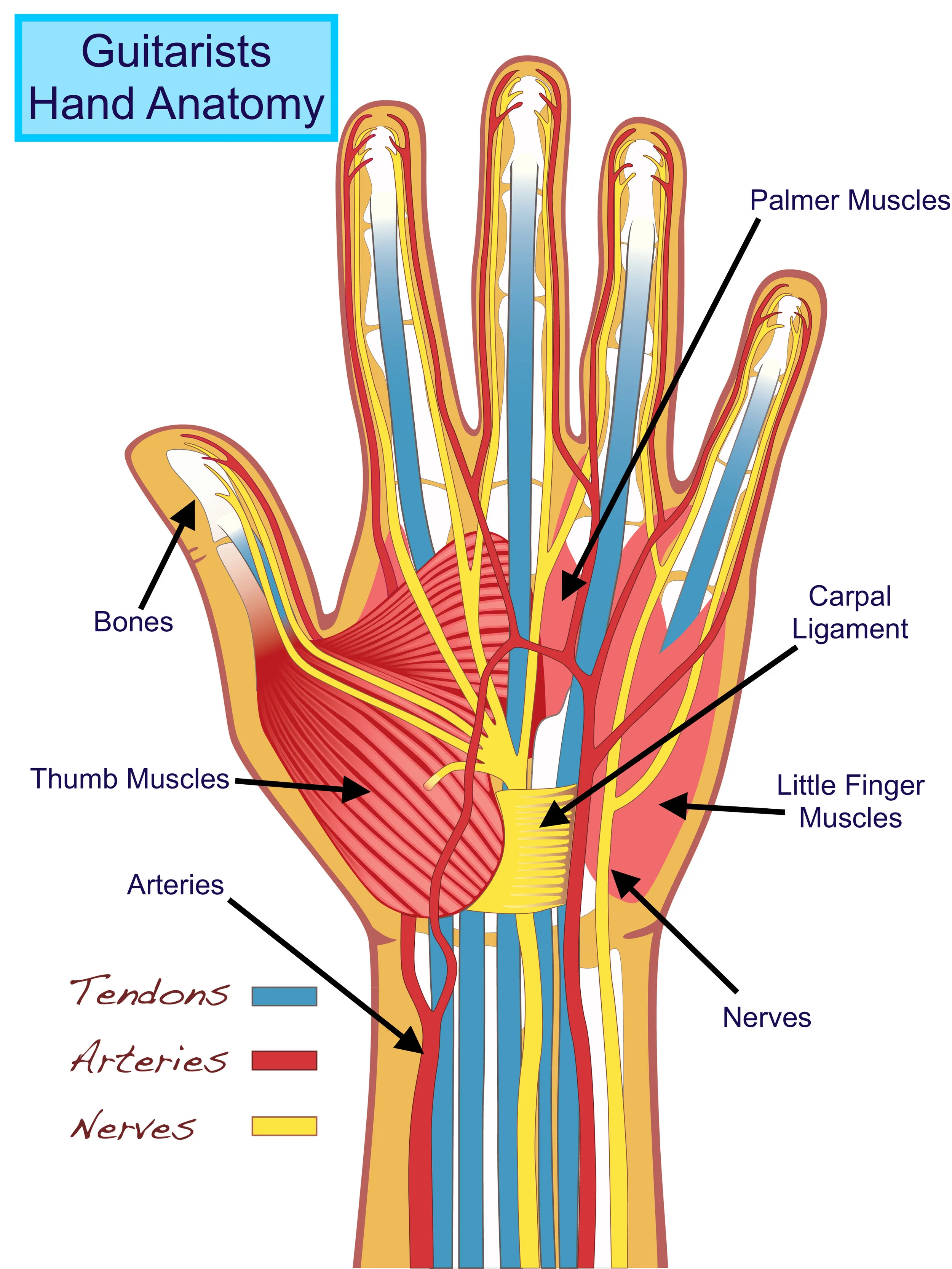
Hand Anatomy — Tuned In Guitar Lessons
The interphalangeal joints of the hand are synovial hinge joints that span between the proximal, middle, and distal phalanges of the hand. In digits 2-5 these joints can be further classified based on which bones are involved. The proximal interphalangeal joint (PIPJ or PIJ) is located between the proximal and middle phalanges, while the distal.

Understanding the Anatomy of the Hand Health Life Media
Human body Muscular System Muscles Muscles The hand has several muscles. Some make broad, smooth movements, and others make small, finite movements. It's the combination of the exterior and.
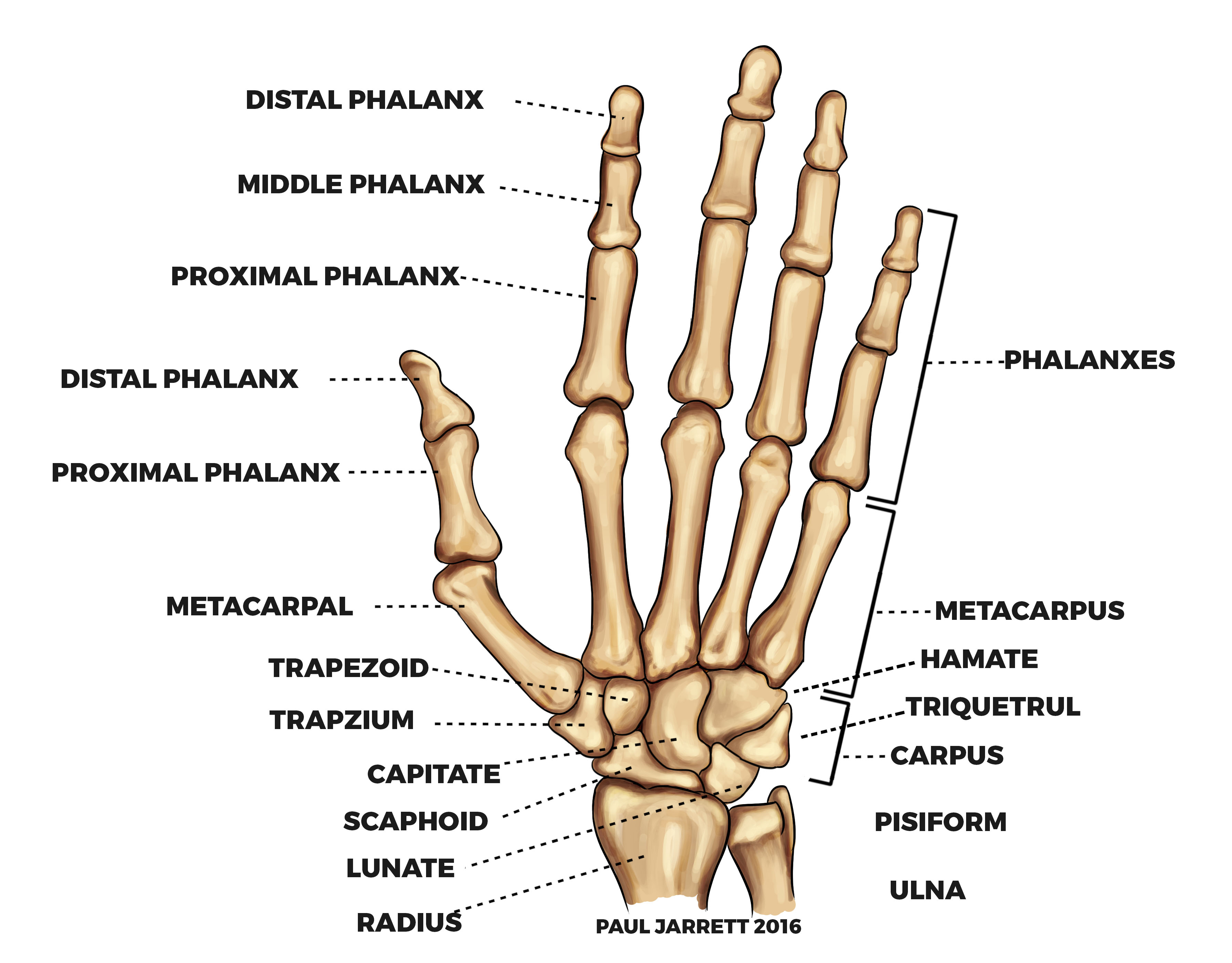
Mr Paul Jarrett Hand and Wrist Anatomy Murdoch Orthopaedic Clinic
Fig 1 - Overview of the bones of the hand. Carpal Bones The carpal bones are a group of eight, irregularly shaped bones. They are organised into two rows: proximal and distal. Collectively, the carpal bones form an arch in the coronal plane.
.jpg?response-content-disposition=attachment)
Hand Bone Diagram resource Imageshare
The hand is located at the distal end of each arm. Apes and monkeys are sometimes described as having four hands, because the toes are long and the hallux is opposable and looks more like a thumb, thus enabling the feet to be used as hands.
Hands and Musculoskeletal Conditions MSK Australia
To understand the anatomy of the hand we first must understand the anatomy of the forearm and wrist. The forearm consists of two bones, the radius and the ulna. Both forearm bones articulate with the carpal bones of the wrist distally. The radius articulates with the cashew shaped scaphoid bone, and the croissant or moon-shaped lunate bone.

Intrinsic Hand Muscles MSK Medbullets Step 1
Palm: This is the bottom of the body of the hand. Back (opisthenar): The back of the hand shows the dorsal venous network, a web of veins. Wrist: The connection point between the arm and the.

Muscles of the Anterior Hand Superficial View Learn Muscles
Anatomy of the Hand Hand and Arm Surgery Orthopedics Anatomy of the Hand The hand is composed of many different bones, muscles, and ligaments that allow for a large amount of movement and dexterity. There are 3 major types of bones in the hand itself, including: Phalanges.

A little about the thumb Therese Milanovic
Hand Bones Anatomy, Functions & Diagram | Body Maps Human body Skeletal System Bones Bones The distal ends of the radius and ulna bones articulate with the hand bones at the.